Services
endoscopic disc surgery
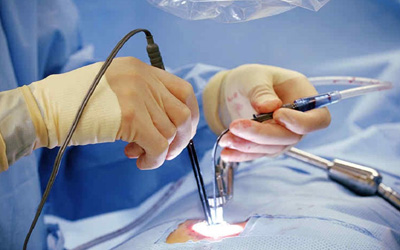
Endoscopic disc surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat conditions involving spinal discs, particularly herniated or bulging discs. This technique utilizes an endoscope—a small, flexible tube with a camera and light—to visualize and operate on the spine through very small incisions.
Common Procedures:
- Endoscopic Discectomy: Involves the removal of herniated or bulging disc material that is pressing on spinal nerves. The endoscope is inserted through a small incision, and the surgeon uses tiny instruments to remove the offending disc material.
- Endoscopic Microdiscectomy: A variation of discectomy that uses an endoscope to remove a small portion of a herniated disc. This procedure is typically used for more specific or localized disc issues.
- Endoscopic Foraminotomy: The endoscope is used to enlarge the foraminal openings where nerves exit the spinal column, relieving nerve compression caused by disc herniation or bone spurs.
Indications for Neurosurgeons:
- Herniated Discs: To relieve nerve root compression and alleviate pain or other neurological symptoms.
- Bulging Discs: When conservative treatments fail, and symptoms are persistent.
- Recurrent Disc Problems: For patients with recurrent disc issues that have not responded to other treatments.
Benefits
- Minimized Tissue Damage: Smaller incisions and less disruption to surrounding tissues lead to reduced postoperative pain and a faster recovery.
- Reduced Scarring: Smaller incisions result in minimal scarring compared to traditional open surgery.
- Faster Recovery: Patients often experience quicker recovery times and shorter hospital stays.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Fewer and smaller incisions reduce the likelihood of infection.
