Services
slipped disc
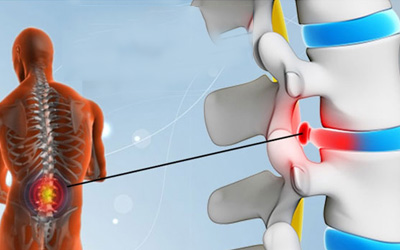
A slipped disc, also known as a herniated disc or prolapsed disc, occurs when the soft inner gel-like core of an intervertebral disc (nucleus pulposus) protrudes through a tear in the outer fibrous ring (annulus fibrosus). This condition can press on the spinal nerves or spinal cord, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness.
Anatomy of the Spine
- Intervertebral Discs: The spine consists of a series of vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs, which act as shock absorbers and allow flexibility.
- Nucleus Pulposus: The inner gel-like core of the disc that provides cushioning.
- Annulus Fibrosus: The tough, fibrous outer layer of the disc that contains the nucleus pulposus.
Causes of a Slipped Disc:
- Age-Related Degeneration: Discs lose hydration and elasticity over time, making them more prone to tearing or rupturing.
- Trauma: Injury to the spine from accidents or falls can cause a disc to herniate.
- Repetitive Strain: Activities that involve repetitive bending, lifting, or twisting can contribute to disc herniation.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of disc herniation may increase the risk.
- Improper Lifting: Using the back muscles instead of the legs to lift heavy objects can lead to a herniated disc
Symptoms:
- Pain: Sharp or burning pain in the affected area, often radiating down the limbs (sciatica if the lower back is involved).
- Numbness and Tingling: Sensations of numbness or tingling in the areas served by the affected nerves.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the affected areas, which can impair the ability to lift or hold items.
- Loss of Reflexes: Diminished reflexes in the arms or legs.
A slipped disc is a common spinal condition that can cause significant pain and neurological symptoms. Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Treatment options range from conservative approaches such as rest, medications, and physical therapy to interventional procedures and surgery for more severe cases. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for relieving symptoms, restoring function, and improving the patient's quality of life.
