Services
hydrocephalus
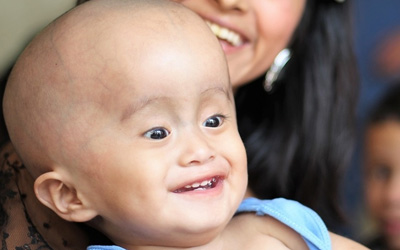
Hydrocephalus is a condition characterized by an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain's ventricles, leading to increased intracranial pressure. This can result in the enlargement of the head in infants and potentially cause brain damage if not treated promptly. Hydrocephalus can affect individuals of any age but is most common in infants and older adults.
Causes:
- Congenital Hydrocephalus: Present at birth and can result from genetic abnormalities or developmental disorders, such as neural tube defects like spina bifida or infections during pregnancy.
- Acquired Hydrocephalus: Develops after birth due to factors such as: Infections (e.g., meningitis), Head injuries, Brain tumors, Intracranial hemorrhage, Complications of surgery.
- Communicating Hydrocephalus: Occurs when CSF flow is blocked after it exits the ventricles, still able to flow between ventricles.
- Non-Communicating (Obstructive) Hydrocephalus: Occurs when the flow of CSF is blocked along one or more of the narrow passages connecting the ventricles.
Symptoms:
In Infants:
- Rapid Head Growth: Unusually fast increase in head circumference.
- Bulging Fontanelle: Soft spot on the top of the head may appear tense or bulging.
- Vomiting: Frequent and forceful.
- Sleepiness: Excessive sleepiness or lethargy.
- Irritability: Increased fussiness and crying.
- Seizures: Episodes of abnormal motor activity.
In Older Children and Adults:
- Headache: Persistent and often worse in the morning.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Especially in the morning.
- Blurred or Double Vision: Due to pressure on the optic nerve.
- Balance and Coordination Problems: Difficulty walking and maintaining balance.
- Cognitive Decline: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and changes in personality.
- Urinary Incontinence: Inability to control bladder function.
Prognosis:
- Infants and Children: Early intervention typically results in a good outcome, though long-term monitoring is necessary. Developmental delays and learning difficulties can occur.
- Adults: Outcomes depend on the underlying cause and timeliness of treatment. Early treatment often leads to better recovery.
- Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH): Common in older adults, characterized by gait disturbance, dementia, and urinary incontinence. Timely treatment can improve symptoms significantly.
Hydrocephalus is a serious condition requiring prompt diagnosis and intervention to prevent long-term brain damage and other complications. Treatment primarily involves surgical options like shunt placement or endoscopic procedures to manage CSF flow. Early recognition and appropriate management are crucial for optimizing outcomes, especially in infants and children. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential to ensure the long-term effectiveness of treatment and to address any complications that may arise.
