Services
spinal dysraphism
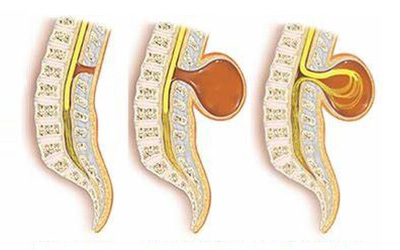
Spinal dysraphism refers to a group of congenital spinal anomalies resulting from incomplete or abnormal development of the spine and spinal cord during embryonic growth. This condition encompasses a variety of defects, ranging from minor to severe, and often involves abnormalities of the vertebrae, spinal cord, meninges, and overlying soft tissues.
Types of Spinal Dysraphism:
- Spina Bifida Occulta: The mildest form, where there is a small gap in the spine but no opening or sac on the back. Often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally on imaging studies.
- Meningocele: A sac of fluid comes through an opening in the baby’s back but the spinal cord is not in this sac. There may be little or no nerve damage, and the individual may have only minor disabilities.
- Myelomeningocele: The most severe form, where a portion of the spinal cord and nerves protrude through the open part of the spine. This form often results in significant disabilities, including paralysis and loss of sensation below the affected area.
- Lipomyelomeningocele: A form of spinal dysraphism associated with a fatty mass attached to the spinal cord. Can cause tethering of the spinal cord, leading to neurological symptoms.
- Diastematomyelia: A condition where the spinal cord is split into two halves, often by a bony or fibrous septum. Can lead to tethered cord syndrome and neurological deficits.
- Tethered Cord Syndrome: Occurs when the spinal cord is abnormally attached within the spine, limiting its movement. Can be associated with various forms of spinal dysraphism and lead to progressive neurological deterioration.
Symptoms of Spinal Dysraphism:
- Neurological Deficits: Weakness or paralysis in the legs, sensory loss, and changes in reflexes.
- Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction: Incontinence or retention issues.
- Orthopedic Abnormalities: Scoliosis, foot deformities, hip dislocation.
- Dermal Signs: Presence of a tuft of hair, dimple, or lipoma over the spine.
- Hydrocephalus: Accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, often associated with myelomeningocele.
Prognosis:
- Varies Widely: Depending on the type and severity of the dysraphism, the timing of diagnosis and intervention, and the presence of associated anomalies.
- Early Detection and Treatment: Crucial for improving outcomes and minimizing long-term complications.
Pediatric neurosurgery plays a critical role in the management of spinal dysraphism. Early diagnosis, timely surgical intervention, and comprehensive post-surgical care and rehabilitation are key to optimizing outcomes and improving the quality of life for affected children. A multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of the child's health and development are addressed, providing the best possible prognosis.
